BRICS em tempos de reacomodação tectônica
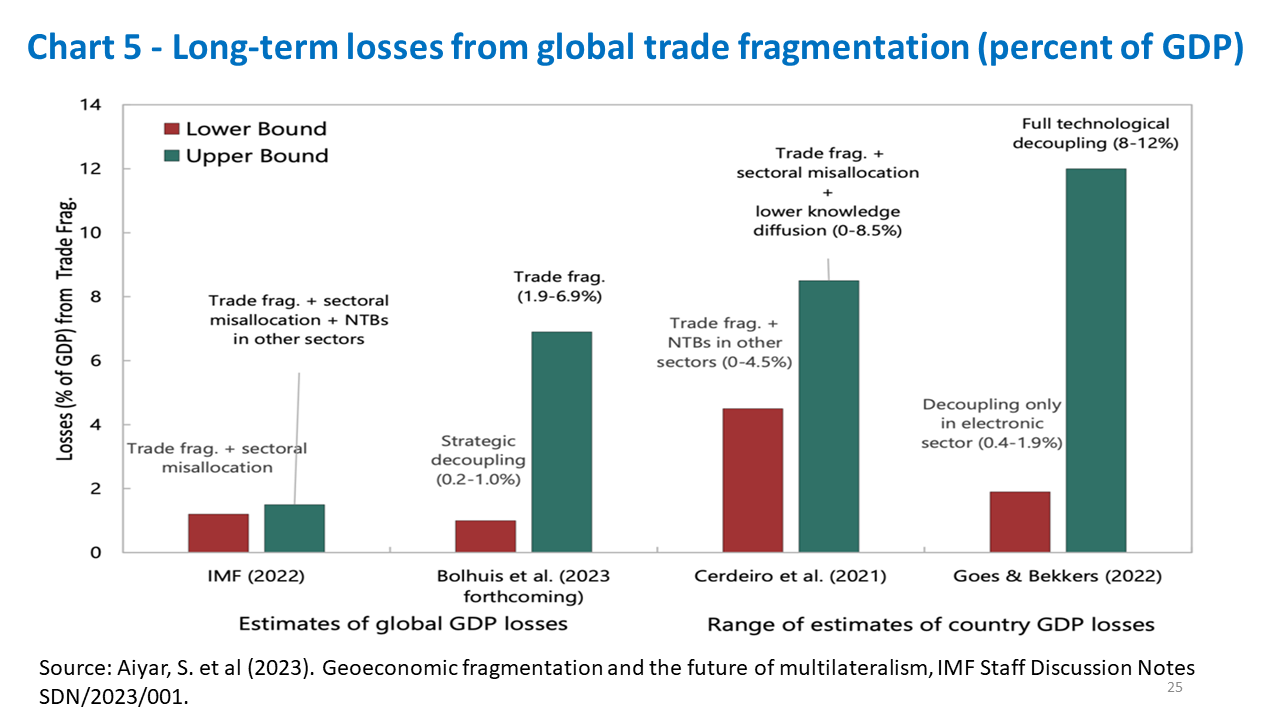
Este artigo avalia o desempenho das economias originais do BRICS relativamente às projeções de crescimento e apreciação cambial apresentadas nos artigos que lançaram o acrônimo antes de o agrupamento se tornar uma realidade diplomática, política e econômica. Na sequência, discutimos a agenda BRICS no atual contexto geopolítico desafiador, no qual a fragmentação econômica tende a elevar custos para a economia mundial e apresenta obstáculos consideráveis para economias emergentes e em desenvolvimento.